
Given an array of size n, find the majority element. The majority element is the element that appears more than ⌊ n/2 ⌋ times.
You may assume that the array is non-empty and the majority element always exist in the array.
Input: [3,2,3]
Output: 3
Input: [2,2,1,1,1,2,2]
Output: 2
1. 알고리즘을 해결하기 위해서 생각한 방법
- 해당 문제는 배열이 주어질 때, 주어진 배열의 크기 n보다, 항상 [n/2] 보다 많은 수가 존재한다.
- 처음 접근 방법은 Map을 사용했다. Map을 통해서 Key에는 원소, Value에는 카운팅의 값을 넣는다.
- 그 후, 해당 Map을 통해서 가장 큰 값을 꺼낸다.
2. 알고리즘 작성 중, 어려운 점
- 어떻게 빠르게 찾지?
3. 내가 작성한 알고리즘
class Solution {
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap();
int max = 0;
int maxElement = 0;
for(int i=0; i<nums.length; i++){
map.put(nums[i], map.getOrDefault(nums[i], 0) + 1);
}
for(Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : map.entrySet()){
if(entry.getValue() > max){
max = entry.getValue();
maxElement = entry.getKey();
}
}
return maxElement;
}
}
4. 내가 작성한 알고리즘 결과
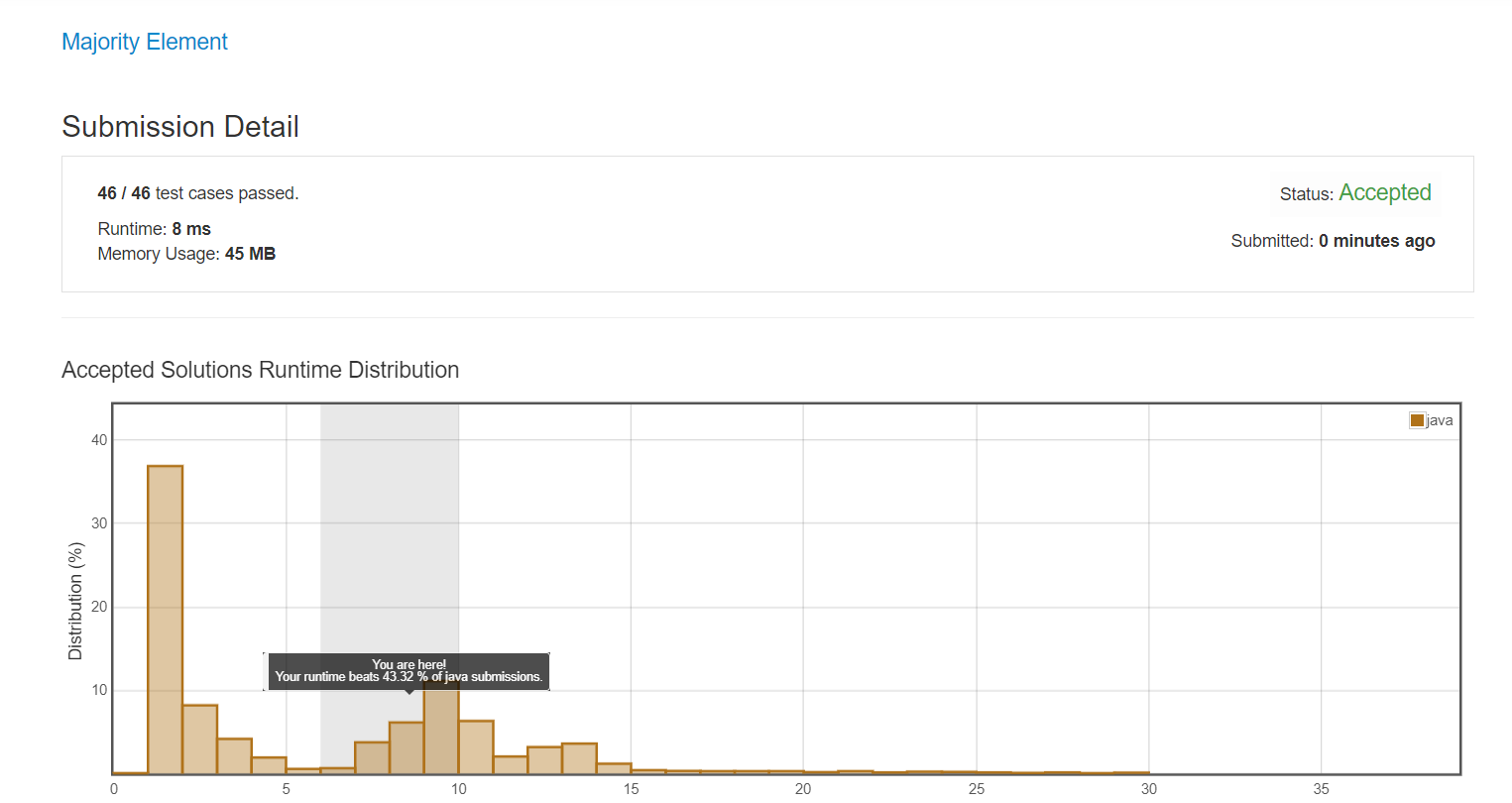
5. 다른 사람이 작성한 알고리즘을 보고 보완하기
- 다른 사람이 작성한 알고리즘을 보고, 문제를 다시 읽어봤다.
- 문제에는 명확한 조건이 하나 있었는데, 당선되는 숫자가 무조건, n / 2 보다 크다는 것이다.
- 이를 활용하게 되면, count의 값을 +,-로 카운팅하게 된다면, 마지막 당선된 숫자는 카운팅만 하더라도, 무조건 자기 자신이 남는다는 사실이다.
class Solution {
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
int major = nums[0];
int count = 0;
for(int i=1; i<nums.length; i++){
if(nums[i] == major){
count++;
}else{
count--;
}
if(count == -1){
major = nums[i];
count = 0;
}
}
return major;
}
}
6. 보완한 결과
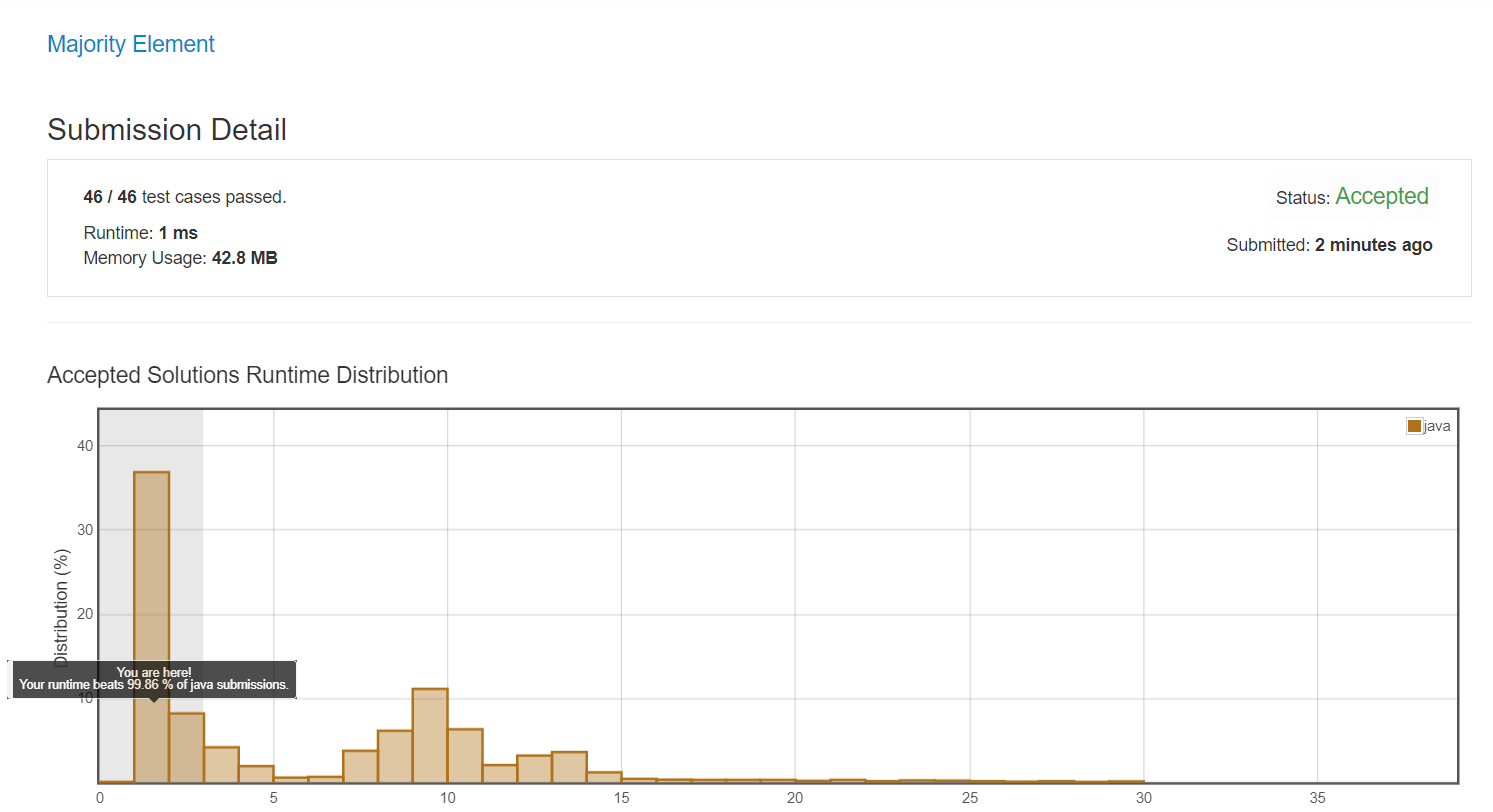
7. 반성할 점
- 문제를 읽으면서, 항상 해왔던 방법이 떠올랐을 때, 그게 느린 방법일 수도 있다는 사실을 생각하자.
문제 : https://leetcode.com/explore/featured/card/may-leetcoding-challenge/534/week-1-may-1st-may-7th/3321/
Explore - LeetCode
LeetCode Explore is the best place for everyone to start practicing and learning on LeetCode. No matter if you are a beginner or a master, there are always new topics waiting for you to explore.
leetcode.com
'내 맘대로 알고리즘 > LeetCode 2020 May' 카테고리의 다른 글
| May LeetCoding Challenge[Day8] - Check If It Is a Straight Line (0) | 2020.05.08 |
|---|---|
| May LeetCoding Challenge[Day7] - Cousins in Binary Tree (0) | 2020.05.08 |
| May LeetCoding Challenge[Day5] - First Unique Character in a String (0) | 2020.05.06 |
| May LeetCoding Challenge[Day4] - Number Complement (0) | 2020.05.05 |
| May LeetCoding Challenge[Day3] - Ransom Note (0) | 2020.05.04 |



